•
Ethernet cable CAT 5e (enhanced): Speed of max 1 Gbps, up to 100 meters long and bandwidth of 100 MHz.
•
Ethernet cable CAT 6: Speed of max 10 Gbps, up to 100 meters long (at 1 Gbps) and 55 meters long (at 10 Gbps) and bandwidth of 250 MHz.
•
Ethernet cable CAT 6a: Speed of max 10 Gbps, up to 100 meters long and bandwidth of 500 MHz.
•
Ethernet cable CAT 7: Speed of max 10 Gbps, up to 100 meters long and bandwidth of 600 MHz.
•
Ethernet cable CAT 8: Speed of max 10 Gbps, up to 100 meters long and bandwidth of 2000 MHz.
Remember to always read the specific product specifications carefully. The maximum length of a cable depends on the shielding of the specific cable. This can affect how far the cable can be. Also, be aware that the newer your cable, the more likely it is to last for many years. If you have made installations in the home, it is always a good idea to go for the latest and greatest. Then there is a greater likelihood that what works now will also work in 10 years.
Choosing the right ethernet LAN cable can be a bit tricky. The easy solution is to choose the largest and most expensive cable, but it is not at all certain that it is the right solution for you. If you are in doubt about which cable suits your needs, you are very welcome to
contact us.If you do not deal with Ethernet cables every day, it can be difficult to remember or know what each letter stands for. We have made a mini dictionary for you here.
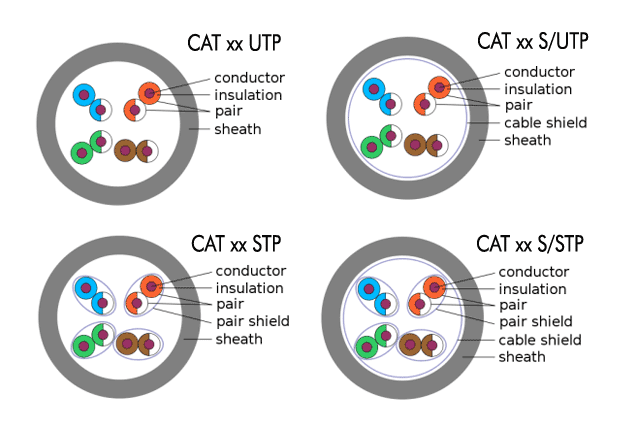
• U = Unshielded.
• F = Foil shielding.
• S = Braided shielding.
• TP = Twisted pair (parvis).
• SQ = Twisted pair, individual shielding in quads (pairwise individually shielded in four pairs).
There are now many types of shielding of network cables, below are the most common. In addition, there are also a corresponding number of variants, where in addition to a normal. shielding is also added a foil shielding, either in the outer sheath or around the paired inner conductors. This will have an "F" in the standard, ie. for example. "SF/UTP" which is a double-shielded network cable where the inner conductors are not shielded in pairs, or e.g. "S/FTP", which means that the cable is single-shielded, and the inner conductors are shielded in pairs with a foil shield.
We carry a wide range of network cables, both with connectors and as cables in loose meters. We have selected an assortment that covers most needs. For example. we have primarily unshielded cables in Cat 5 and 6 (UTP), double shielded versions of Cat 6, Cat 6a and Cat 7 (S/FTP), which is most often the most profitable version with a very high shielding immunity.
The standard for the general. The most commonly used form of network is Ethernet. An Ethernet signal is often transmitted through a network cable with RJ45 connectors mounted at both ends, also known as modular 8P8C connectors. Before Ethernet, the most common network system was
IBMs Token Ring (IEEE 802.5, up to 16 Mbit), but it belongs to the past.
In newer type
HDMI cables, an Ethernet signal also carried from device to device, directly in the HDMI cable without the use of normal. network cables; however, it requires the equipment supporting it.
